Today, many Russians go abroad, often to European countries, for the purpose of work, study or permanent residence. Of course, in those states in which the welfare of citizens is higher, wages are also higher. Knowing what is the average salary in Europe today, it is easier to decide where to go in search of a better life. The average level of income of citizens is one of the indicators of the development of the economy of the state as a whole, and therefore, evidence of stability, high level and quality of life.
Payroll rules in European countries
In Europe, it is customary to pay for the work of employees by the hour. It is believed that this is the fairest way of remuneration, therefore it is practiced in all countries of the European Union. For example, migrants employed in Italy, Spain or the UK can choose a work schedule that suits them: part-time or work on weekends. In this case, the employee will know that he will receive a salary strictly for the time he has worked.
European salary statistics
Official data on the average salary in the EU countries is annually collected and presented on its portal by the Eurostat service. Data on salaries in European countries as of 2021 are shown in the table:
| Country | Payment for 1 hour of work in the private sector, euro | Payment for 1 hour of work in the industrial sector, euros | Average monthly salary in euros | Average monthly salary in rubles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belgium | 40,60 | 43,30 | 4511,11 | 357082,00 |
| Bulgaria | 4,70 | 3,70 | 637,29 | 50423,00 |
| Czech Republic | 10,70 | 10,10 | 1249,64 | 98868,00 |
| Denmark | 44,00 | 43,40 | 6068,97 | 480331,00 |
| Germany | 30,50 | 38,70 | 3812,50 | 301750,00 |
| Estonia | 11,50 | 10,60 | 1352,94 | 107021,00 |
| Ireland | 28,10 | 31,30 | 3810,17 | 301592,00 |
| Greece | 13,80 | 14,60 | 1588,49 | 125703,00 |
| Spain | 20,40 | 22,80 | 2417,78 | 191325,00 |
| France | 36,10 | 37,60 | 3929,25 | 311012,00 |
| Croatia | 9,30 | 7,60 | 1261,0 | 99818,00 |
| Italy | 26,90 | 27,30 | 3141,61 | 248635,00 |
| Cyprus | 16,30 | 12,90 | 2173,33 | 172010,00 |
| Latvia | 8,30 | 7,10 | 1053,97 | 83353,00 |
| Lithuania | 7,70 | 7,10 | 880,00 | 69659,00 |
| Luxembourg | 39,60 | 31,10 | 5462,07 | 432361,00 |
| Hungary | 8,60 | 8,20 | 1066,67 | 84382,00 |
| Malta | 12,80 | 12,60 | 1878,90 | 148659,00 |
| Netherlands | 32,30 | 35,10 | 3975,38 | 314653,00 |
| Austria | 31,50 | 35,50 | 3705,88 | 293280,00 |
| Poland | 8,50 | 7,70 | 1114,75 | 88182,00 |
| Portugal | 14,30 | 11,30 | 1801,57 | 142563,00 |
| Romania | 5,80 | 4,70 | 742,40 | 58735,00 |
| Slovenia | 16,50 | 15,90 | 2218,49 | 175572,00 |
| Slovakia | 10,70 | 10,60 | 1258,82 | 99580,00 |
| Finland | 32,00 | 37,0 | 4031,50 | 319086,00 |
| Sweden | 40,40 | 41,90 | 4338,26 | 343388,00 |
| United Kingdom | 25,90 | 25,40 | 3482,35 | 275628,00 |
| Iceland | 23,03 | 23,17 | 2058,00 | 162907,00 |
| Norway | 53,83 | 56,38 | 7094,00 | 561547,00 |
| Switzerland | 52,48 | 51,25 | 8148,00 | 644980,00 |
| Montenegro | 5,54 | 5,81 | 844,00 | 66809,00 |
| Albania | 2,41 | 2,20 | 422,00 | 33404,00 |
| Serbia | 5,25 | 5,12 | 723,00 | 57231,00 |
| Turkey | 6,84 | 6,26 | 1245,00 | 98551,00 |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 5,65 | 5,29 | 861,00 | 68155,00 |
The labor costs shown in the table are the total costs of the employer. The amount includes gross wages (wages), "net" wages, employer's social insurance contributions, training or other expenses, employment taxes. These salary components are defined by the EU Commission Regulation No. 1737/2005 of 21.10.2005.
What does a salary card look like in Europe
The European Salary Map has been compiled based on the average annual salary of EU citizens.
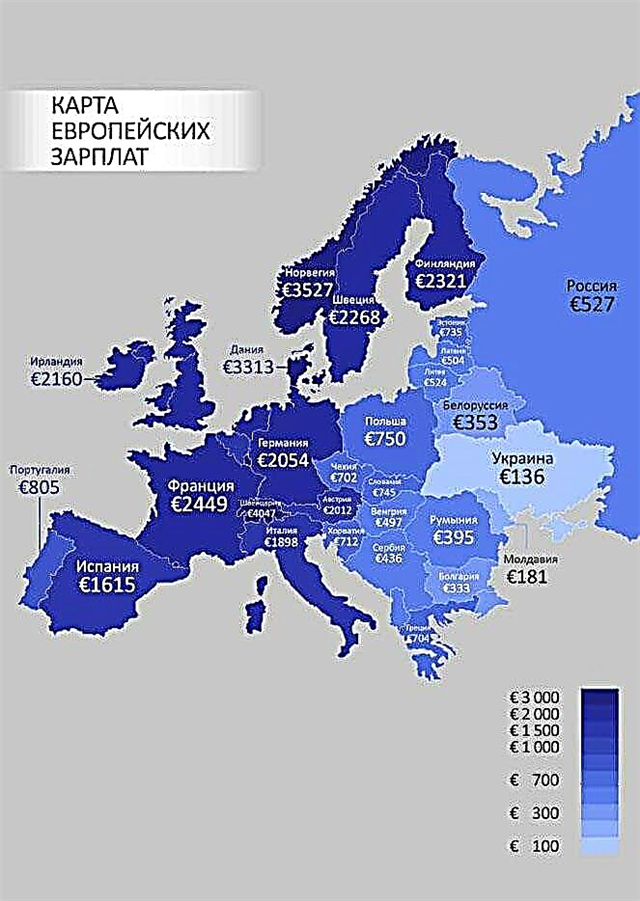
Less intense coloration means a lower salary. It should be noted that the presented list of European countries in terms of wages reflects the "net" average monthly earnings in the EU countries, that is, the amount that the employee receives in his hands:
- dark blue - 3000 €;
- blue - 1000-2000 €;
- less intense blue - 300-1000 €;
- soft blue - below 300 €.
The ranking of salaries in Europe by employee income per hour is as follows:
- lowest hourly salary:
- in Albania - 2.41 euros;
- Bulgaria - 4.70 euros;
- Serbia - 5.25 euros;
- Montenegro (Montenegro) - 5.54 euros;
- Bosnia and Herzegovina - 5.65 euros;
- highest salaries per hour of work:
- in Norway - 53.83 euros;
- Switzerland - 52.48 euros;
- Denmark - 44.00 euros;
- Belgium - 40.60 euros;
- Sweden - 40.40 euros.
However, quite often the average indicator of the amount received by an employee for work does not reflect the real state of affairs. For example, in order to find out exactly what wages are in Eastern Europe, it is important to take into account the productivity of workers.

If on average the cost of labor is 4 times lower than in Germany, then labor productivity, according to Bloomberg and Eurostat, is much higher. The source sites also provide a table of wages in Europe in terms of PPP in 2021 (purchasing power parity). In it, the Russian Federation takes 69th place in the list. The first in the ranking is Switzerland ($ 3,855 net one per employee).
In addition, wages in the EU depend on the qualifications and experience of the employee. So, the minimum wage in industry in Europe is 7-8 € per hour of work. For example, in Finland, an electrician, fitter, locksmith or other similar specialists can earn 2-3 thousand euros per month.
How much do Europeans get on average?
The average salary in Europe in euros per month is as follows (in increasing order):
- Albania - 422 € / month This is the lowest average wage in Europe;
- Bulgaria - 637 € / month;
- Serbia - 723 € / month;
- Romania - 742 € / month;
- Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Lithuania - 840-880 € / month;
- in Hungary, Latvia, Turkey, Slovakia, Poland, Portugal, Malta, Croatia, Greece, Estonia, the Czech Republic, on average, they receive from 1 to 2 thousand euros;
- in Iceland, Slovenia, Cyprus, Spain salaries slightly exceed 2 thousand euros (up to 3000 €);
- in Germany, France, Italy, Austria, the Netherlands, Great Britain, the average salary is 3-4 thousand euros per month;
- in Belgium and Sweden - average earnings from 4 to 5 thousand euros;
- the highest average salaries from 5 thousand euros (over 400 thousand rubles) in Luxembourg - € 5462, Denmark - € 6068, Norway - € 7094, Switzerland - € 8148.
When talking about average wages, it should be borne in mind that taxes in Europe often “eat up” most of the income. So, in Sweden, the income tax rate is 56.4%, that is, more than half of the earnings goes to the state.
In Belgium, the tax is 53.7%, in the Netherlands - 52%, in Denmark - 51.5%, in the UK - 50%. The European average tax rate is 33%, the minimum tax is 10% in Bulgaria.
Minimum wages in Europe
The legal minimum wage in Europe varies widely from country to country. Its highest rate was recorded in Luxembourg - the "minimum wage" here is almost 2000 euros (€ 1922.96).
In Belgium, according to statistics, this figure is 1501.82 €, in the Netherlands it is almost the same - 1501.80 €.

In Germany, workers receive a minimum of € 1,473.00 and in Ireland € 1,461.85.
The fifth largest is the minimum wage in France - 1457.52 €, the sixth - the "minimum wage" in the UK, amounting to 1378.87 €.
Slovenia takes the first place in terms of the size of the minimum wage among the EU countries in a state of crisis (Spain, Greece, Portugal), as well as the states of the former socialist camp. Here, citizens receive a minimum of € 790.73. In Spain, this figure is 756.70 €, in Greece - 683 €, in Portugal - 589 €, in Poland - 409.53 €, in Montenegro - 288 €, in Serbia - 235 €.
The two countries with the lowest "minimum wages" in the European Union are Romania and Bulgaria, where income is € 217.50 and € 184.07, respectively.
Top 10 European Countries with the Highest Average Salary
Salaries in Europe are very different. And although the amount of income of citizens in each country is determined by many factors, it primarily reflects the state of the state's economy. According to statistics, the largest salaries in Europe in 2021 were recorded in the following countries:
- Switzerland - 95,178 € / year;
- Norway - 89725 € / year;
- Sweden - 62,922 € / year;
- Belgium - 55356 € / year.
- France - 52938 € / year.
- Austria - 51,455 € / year.
- Finland - 50337 € / year.
- Germany - 50,025 € / year.
- Ireland - 49409 € / year.
- Great Britain - 46799 € / year.
Switzerland, which for a long time has not been inferior to the palm in terms of income of citizens, despite its small size, has a well-developed banking system and is famous for high-quality production of goods. At the same time, the country owes a constant influx of tourists to receive a significant amount of additional funds.
How much do workers of different professions get in Europe
The shortage of specialists in each country is felt differently. Accordingly, the distribution of salaries by occupation in Europe is not the same.
For example, in Norway, doctors, IT specialists, programmers, and employees of oil companies have the highest earnings. In Germany, computer specialists, financiers, doctors, and employees of insurance companies are well paid.In France, IT workers, accountants have big salaries, workers in production have good wages.
Russians often go to Europe to work. Among them, the most in demand are representatives of blue-collar professions: builders, handymen, nannies, nurses, drivers, service personnel, agricultural workers.

The average salary in rubles for such positions averages from 39,000-62,000 (€ 500-800) to 156,000 rubles (€ 2,000).
In general, salaries in Europe by occupation are distributed as follows:
- financiers - salary 101 thousand US dollars;
- senior manager –133 thousand dollars;
- lawyer - 80-93 thousand dollars;
- engineer-economist - from 20 thousand dollars in Belgium to 40 thousand dollars in Switzerland;
- IT specialist - from 20 thousand dollars in Belgium, Italy to 40 thousand dollars in Switzerland.
How much is paid for work in Europe and in Russia
According to statistics, the average salary in Russia in 2021 is 33,408 rubles. In terms of European currency, this will be about 425 euros per month. As noted above, from all European countries the same salary as in Russia, only in Albania. With the rest of Europeans, the difference in salaries for Russians is quite significant - from 200 to 7000 € per month.
As for the hourly wages, in the Russian Federation it is approximately equal to the salary in China and amounts to 0.8 dollars per hour, or 0.68 euros, or 53 Russian rubles.
The international statistical agency Fitch estimates the salaries of Russians 2.5 times less than in Germany and 30% less than in Lithuania.
Despite the fact that in 2021 in the Russian Federation there is an increase in real wages of citizens by 3-4%, in terms of purchasing power parity (that is, the possibility of purchasing goods and services of certain categories), the income of Russians still loses to the European one.

In addition, if we compare salaries in Russia and Europe, one should take into account the spread of incomes of Russians: according to statistics, residents of the capital receive, according to statistics, an average of 92,000 rubles (1,200 euros), while in the provinces, wages are 7-8 thousand rubles (90– 100 euro).
For example, if we compare how much a teacher gets in the Russian Federation and in the EU, we get the following: Germany - 337 thousand rubles. ($ 5110), Spain - 224 thousand ($ 3396), the Netherlands - 211 thousand ($ 3206), France - 168 thousand ($ 2554), Greece - 97 thousand ($ 1480), Russia - 31 thousand ($ 477).
The salary of a police officer in Russia is also much less than in Europe. So, in Germany, the monthly income of a police officer is 220 thousand ($ 3349), in Poland - 62 thousand ($ 937), in Lithuania - 54-77 thousand ($ 800-1000), in Bulgaria - 94 thousand ($ 1428) , in Russia - on average 40 thousand ($ 608). Police salaries are approximately equal only in the Russian Federation and Kazakhstan, where the salary of a law enforcement officer is about 39 thousand ($ 595).
Finally
Comparison of the level of wages in Europe and Russia shows that payments to workers in the Russian Federation are much lower than abroad. Even in spite of the significant spread in salaries in European countries, the average income of Russians does not reach the level of European ones.
The most generous countries in terms of remuneration for work have been Switzerland, Luxembourg, Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Belgium for many years. At the same time, when going abroad to earn money, one should take into account the amount of taxes on wages in the country where employment is planned.