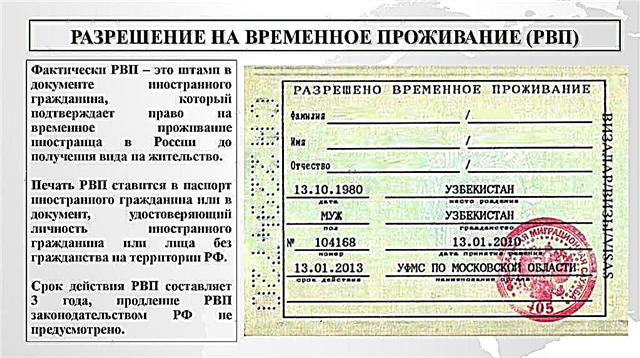
Termination of citizenship means that a person loses the corresponding status of belonging to the state, but retains or acquires the status of a citizen of another country or stateless person (not belonging to any other country).
Grounds for the acquisition of belonging to the Russian Federation
The issues of acquisition and loss of citizenship are regulated by such a normative act as Federal Law No. 62-ФЗ dated May 31, 2002, the last updated version of which is dated July 29, 2017. Chapter 2 is devoted to this, and chapter 3 is devoted to its termination. To find out what are the rules for conducting this process, you need to refer to Art. 11 FZ.
The grounds for obtaining the status are:
- The status is acquired at birth (Article 11 of the Federal Law No. 62), for this you need at least one parent to be a Russian citizen;
- It is acquired as a result of a special admission procedure (in the usual or simpler version);
- Due to recovery;
- Other circumstances that are contained in Federal Law No. 62 or in international treaties of the Russian Federation.
Law No. 62-FZ sets out the grounds for obtaining membership in the Russian Federation in a simplified version. A list of them is given in Chapter 2. In a general sense, a simplified version is a procedure that is not associated with long-term residence in Russia (5 years after obtaining a residence permit).

In a simplified version, the desired status can be obtained by:
- Born in Russia;
- Born in USSR;
- Spouse of a Russian (if the marriage is at least 3 years old);
- Parent of a Russian (subject to certain conditions stipulated in Art. 14);
- Refugee;
- Highly qualified specialist;
- Forced migrant;
- Citizen of the CIS country;
- Trained in the Russian Federation or the USSR;
- Russian native speaker;
- Investor subject to a certain amount of tax contributions at the time of circulation (6 million rubles) and net assets (not less than 100,000,000 rubles);
- WWII veteran;
- Citizen of Kyrgyzstan, Belarus, Kazakhstan.
The rest of foreign citizens and stateless persons receive citizenship according to general rules.
Restoration in civil status (Article 15) means that those who previously had legal belonging to the Russian Federation can get it back in a shortened period (it is understood that the required residence in the territory of the Russian Federation is reduced from 5 to 3 years).
Acquisition of Russian citizenship
Regardless of the option (general or simplified), the algorithm of action is approximately the same. It can be briefly presented as follows:
- Determination of the grounds for obtaining the corresponding position;
- Identification (based on the first point) of a suitable option (general or simplified);
- Collection of documents required in accordance with the selected procedure;
- Writing a statement;
- Payment of the state duty (according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the state duty will be 3500 rubles);
- Refusal of citizenship of another country (except for citizens of Turkmenistan and Tajikistan: with these countries, Russia has concluded corresponding agreements);
- Sending documents to the territorial department of the UVM of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, receiving a certificate in return;
- Taking the oath;
- Obtaining a Russian passport.
You May Also Like
In the general and simplified version, only the documents accompanying the application and the period of consideration will differ (simplified form - 3 months - 6 months, in other cases - 1 year).
Grounds and methods of termination
Chapter 3 of the Federal Law No. 62 establishes the following grounds (methods):
- Withdrawal from citizenship;
- Other circumstances.
The latter should be provided for either by the legislation of the Russian Federation (No. 62-FZ), or by agreements between Russia and other countries. For example, as provided for by Art. 21 of the Law, in the event of a change in the borders of the Russian Federation, citizens have the right to choose themselves whether to remain in the same position of Russians or change it in favor of another country.
On a voluntary basis
Voluntarily, membership in the state in Russia is terminated as a result of a person's personal choice or when state borders change.
The rules for voluntary withdrawal are regulated by Chapter 3 of Law No. 62. This procedure provides for:
- General order.
- Simplified.
In addition, there is a procedure for the loss of the relevant position by minors at the request of their parents or one of them (part 3 of article 19). In this case, simpler conditions apply.
Forcibly
Actually, this cannot be done forcibly. The right to belong to the state is protected by the Constitution of the Russian Federation. But at the same time, the state has the right to annul the decision of admission to the ranks of Russian citizens in cases established by law.
That is, only the revision of the decision to acquire citizenship can be considered compulsory deprivation. This is possible only if you provide deliberately incorrect information about the identity of the acquirer's citizenship or if the Oath is not taken (Article 22).
You May Also Like
Termination procedure
This procedure in Russia is provided for by chapters 3 of Law No. 62-FZ (voluntarily) and chapter 4 (compulsory).

On a voluntary basis
You should be aware that voluntary termination cannot be achieved if:
- Legally defined obligations to the RF have not been fulfilled;
- The person is charged with a criminal offense or has been sentenced in a criminal case;
- A person does not belong to another state and is not expected.
In these cases, the person will have to remain in the existing position until the problems that prevent the renunciation of citizenship are resolved.
This is done voluntarily as follows:
- By filing an application (general view);
- By registration (an easier way to exit).
In the latter case, it is necessary that the applicant has a child or a parent who is a citizen of another state, or that the person leaves for permanent residence in another territory (and formalizes this according to legislatively established rules, including international treaties).
Forcibly
Deprivation of the acquired position is forcibly carried out by the President (or other authorized body). After consideration by the specified person or body of the decision on the assignment of citizenship and its invalidation, the person is deprived of the relevant position.
The termination of citizenship, like the acquisition, is carried out on the conditions established by the current legislation. It is possible both voluntarily - with a personal expression of will, a change in the state borders or a statement by parents (in cases with minors), and compulsorily - as a result of the discovery of the submission of false information when entering into citizenship or failure to take the Oath of the Russian Federation. Also, the law establishes a number of circumstances that prevent the refusal from belonging to the state.